Cloud Computing has become an indispensable technology for businesses of all sizes, widely integrated into daily operations. While initially perceived as a technological revolution, it has now become an integral part of the modern IT landscape. Cloud allows organizations to access IT services such as data storage, applications, or computing power via remote servers, without the need to invest in complex physical infrastructure.
The adoption of Cloud Computing has profoundly changed how businesses manage their IT resources. Thanks to its flexibility, scalability, and optimized costs, the cloud has become an essential strategic lever. From startups to multinational corporations, including the public sector, this technology offers a simple and effective solution to meet the growing demands for performance, security, and data accessibility.
Sommaire
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing emerged in the 2000s as a response to the growing needs of businesses for flexibility, scalability, and cost reduction. Previously, companies had to make significant investments in physical servers and complex IT infrastructures to store their data and run applications. While these systems were effective, they represented a heavy investment in terms of purchasing, maintenance, and upgrading costs.
The rise of cloud computing changed this situation by offering an online solution where IT resources such as storage, computing, and applications are provided by remote servers accessible via the internet. This model not only eliminated the need for costly local infrastructure but also allowed for more flexible and scalable data management.
Cloud computing relies on virtualization technology, which allows physical resources to be shared across multiple remote servers. Instead of purchasing and maintaining individual servers, a company can access a shared virtual infrastructure, in a flexible, on-demand manner. This “on-demand” model allows businesses to rent only the resources they need, based on their current needs, and quickly adjust these resources as demand evolves.
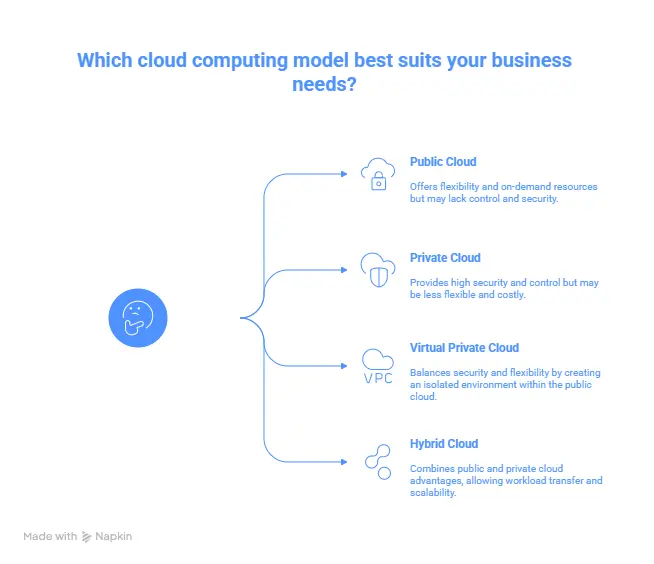
Different types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing takes several forms tailored to business needs. Each of these forms offers distinct advantages in terms of control, security, and flexibility.
Public Cloud
The public cloud is the most common form of cloud computing. In this model, IT services are hosted on public servers and are accessible via the internet. Providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform offer computing and storage resources in a flexible, on-demand manner.
Private Cloud
The private cloud is a model where a business retains full control over its resources and data, often using dedicated servers. This model is commonly adopted by large enterprises that require a high level of customization, security, and control.
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
The Virtual Private Cloud offers a hybrid solution, combining the security of a private cloud with the flexibility of a public cloud. It allows for the creation of an isolated environment within the public cloud, ensuring a high level of security and control while benefiting from the flexibility of the cloud.
Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud combines multiple types of clouds, allowing businesses to benefit from both the public and private cloud advantages. This enables the transfer of workloads between clouds based on specific needs, creating a more flexible and scalable IT environment.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers many benefits for businesses of all sizes. These benefits, covering both financial and technical aspects, help companies optimize their processes while reducing costs.
Cost optimization
One of the major advantages of cloud computing is the reduction of IT infrastructure costs. Unlike a traditional model where a company must invest heavily in servers and infrastructure, the cloud allows businesses to pay only for what they use. This pay-as-you-go model offers great flexibility and allows for better resource management.
Scalability and flexibility
Cloud enables businesses to quickly adjust their resources based on their needs. Storage and processing capacities can be increased or decreased in just a few minutes, offering unparalleled flexibility, especially during peak periods.
Reliability and accessibility
Thanks to virtualization, cloud computing services are highly reliable. In case of a server failure, the service can automatically switch to another server without interruption for the user. Additionally, these services are accessible from anywhere, at any time, on any device connected to the internet, facilitating remote work and distributed teams.
Risks and challenges of Cloud Computing
Despite its many advantages, cloud computing also presents challenges that businesses must be mindful of. These risks mainly concern security and dependency on the provider.
Data security
Data security in the cloud remains a major concern for many businesses. While cloud providers invest heavily in security technologies, there are still risks related to unauthorized access, data loss, and privacy breaches. It is essential for businesses to review the terms of service and ensure that the provider offers adequate security guarantees.
Internet dependency
Cloud computing relies on a stable internet connection, and an outage or disconnection could render services inaccessible. Additionally, dependency on a single provider poses a risk in case of provider failure, or if the company decides to switch providers.
Conclusion
Cloud computing represents a major technological shift for businesses. It not only helps reduce costs and increase flexibility but also offers access to powerful IT resources without the need to invest in costly infrastructures. However, to fully benefit from it, companies must carefully choose their cloud providers and implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data.
Dreyfus & Associés is partnered with a global network of intellectual property attorneys. Our expertise allows us to effectively assist you in managing the legal challenges associated with adopting cloud computing.
Nathalie Dreyfus with the help of the entire Dreyfus team.
FAQ
What is cloud computing and how does it work?
Cloud computing allows businesses to access IT services (such as storage, computing, or applications) via the internet, using remote servers. Instead of investing in costly physical infrastructures, businesses can rent these services on-demand based on their needs.What are the main types of cloud computing?
There are several types of cloud computing:
- Public Cloud: Services hosted on public servers, accessible via the internet.
- Private Cloud: Infrastructure dedicated to a single business, offering full control.
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): Combines the advantages of both private and public clouds, with a secure environment.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combines multiple types of clouds, offering flexibility and security.
What are the main benefits of cloud computing for businesses?
Benefits include cost reduction, scalability (the ability to add or reduce resources as needed), and increased accessibility, allowing employees to work from anywhere, at any time, on any device.
What are the risks associated with using cloud computing?
Risks include data security, particularly the potential for unauthorized access or privacy violations, and dependency on the internet and the service provider. A failing internet connection or a provider facing issues can cause service interruptions.
How can data security be ensured in the cloud?
To ensure data security, it’s crucial to choose a reputable cloud provider, use encryption technologies, and verify the security guarantees provided in the service terms. Businesses should also implement strict access and data management policies.