Sommaire
Introduction
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the legal frameworks governing the protection of intellectual property rights are continuously evolving to keep pace with this global integration. Intellectual property laws in place ensure that the creators of these works are properly recognized and compensated for their efforts. International intellectual property laws are designed to protect the rights of creators and inventors around the world.
The main international treaties and conventions
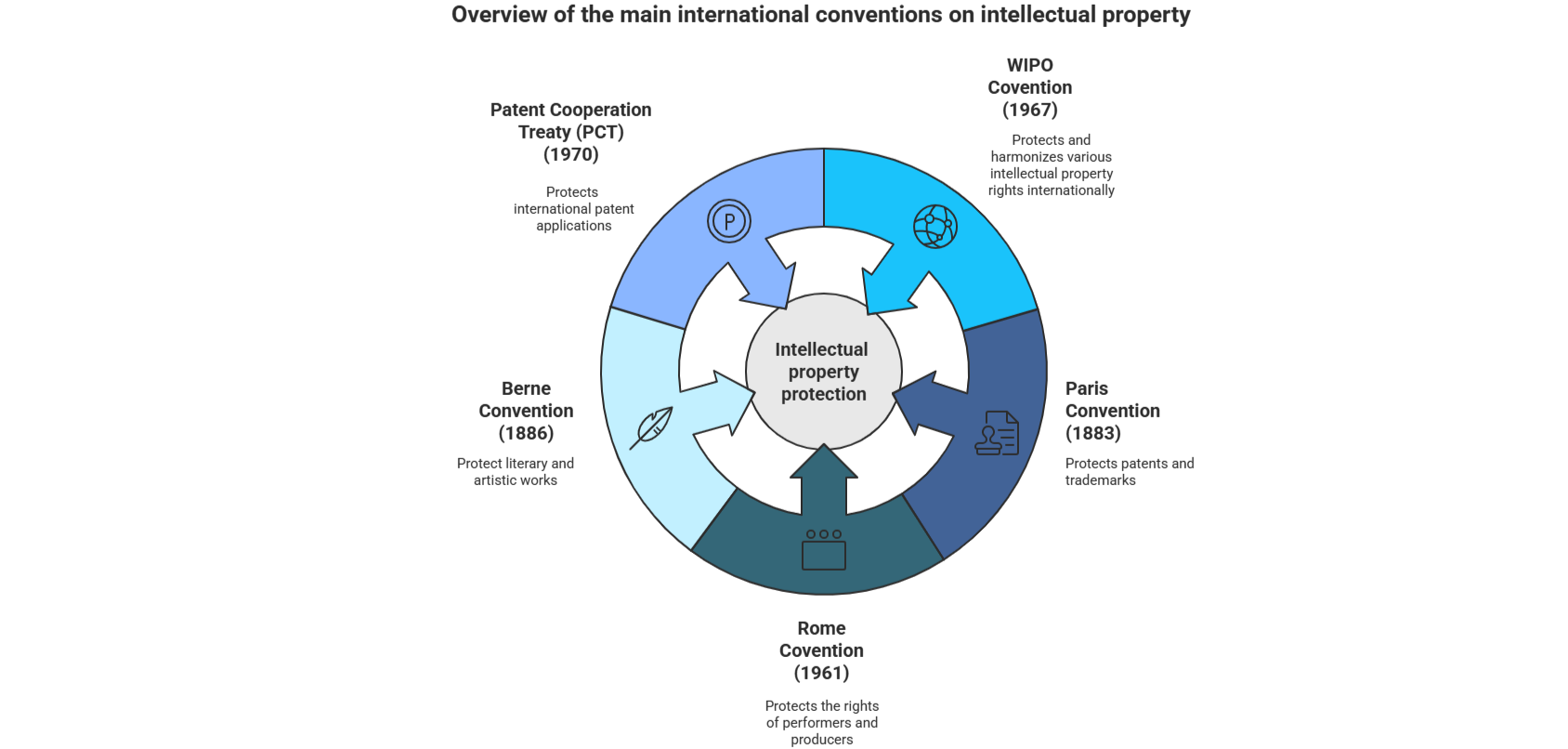
The most widely accepted international intellectual property law is the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) Convention. This treaty was signed by 169 countries in 1967 and updated in 1996. It outlines the rights of inventors, authors, and other creators of intellectual works. WIPO is the international authority that administers the Convention, which sets out the basic principles and rules of international intellectual property law. It also provides a framework for international cooperation on intellectual property issues and seeks to harmonize the different national intellectual property laws.
The WIPO Convention is supplemented by other treaties, such as the Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property (1883), the Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Artistic Works (1886), and the Rome Convention for the Protection of Performers, Producers of Phonograms and Broadcasting Organizations (1961). These treaties are designed to help protect intellectual property rights in different types of works, such as artistic works, designs, and sound recordings.
Learn more about the Paris Convention or visit the WIPO website
Another key instrument for patent protection is the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) (1970). Administered by WIPO, the PCT allows inventors, through a single filing, to submit one. single patent application to seek patent protection in multiple countries simultaneously, thereby greatly simplifying procedures and reducing costs.
The Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) is another important international intellectual property law. This agreement, which was developed by the World Trade Organization (WTO), sets out the minimum standards for intellectual property protection that must be met by WTO member countries. It requires countries to provide certain levels of protection for patents, copyrights, trademarks, and other forms of intellectual property.
Learn more WTO-TRIPS.
The regional and national dimensions
In addition to these international intellectual property laws, there are also regional agreements that provide protection for intellectual property rights. The European Union, for example, has its own set of laws that protect intellectual property rights. The European Union Intellectual Property Rights Directive seeks to harmonize the rules governing the protection of intellectual property in the EU (Directive 2004/48/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 on the enforcement of intellectual property rights).
Conclusion
In summary, a body of international, regional, and national rules governs the protection of the rights of authors, inventors, and other creators of intellectual works. These legal frameworks aim to ensure the effective recognition of their rights and to provide fair remuneration in return for their creations.
Dreyfus Law firm assists its clients in managing complex intellectual property cases, offering personalized advice and comprehensive operational support for the complete protection of intellectual property. Dreyfus Law firm is partnered with a global network of lawyers specializing in intellectual property. Nathalie Dreyfus with the assistance of the entire Dreyfus team.
FAQ
1.What is the WIPO and what is its role ?
The WIPO (World Intellectual Property Organization) is a United Nations authority responsible for promoting the protection of intellectual property worldwide. It administers several international treaties, including the Paris Convention and the Berne Convention.
2.What is the difference between the Berne Convention (1886) and the Paris Convention (1883) ?
The Berne Convention protects literary and artistic works (copyright), while the Paris Convention focuses on the protection of industrial property (such as patents, trademarks, and industrial designs).
3.Are intellectual property rules harmonized worldwide?
Not exactly. There are international treaties to harmonize the rules, but each country has its own national legislation. The TRIPS Agreement sets minimum standards that must be followed by all WTO member countries (World Trade Organization).
4.Where can the various legislative texts and international treaties on intellectual property be consulted ?
The TRIPS Agreement can be accessed on the World Trade Organization (WTO) website.