Sommaire
Introduction
In an increasingly globalized digital market, Universal Acceptance (UA) has emerged as a fundamental standard for businesses and legal professionals. Universal Acceptance ensures that all domain names and email addresses regardless of script, language, or character length are recognized and supported by all applications, devices, and systems connected to the Internet. This inclusivity is not merely a technical requirement, but a strategic necessity for organizations seeking to expand their digital presence and engage with diverse, multilingual audiences.
Understanding universal acceptance
Universal acceptance is a foundational principle that guarantees the interoperability of all valid domain names and email addresses across the Internet. It includes:
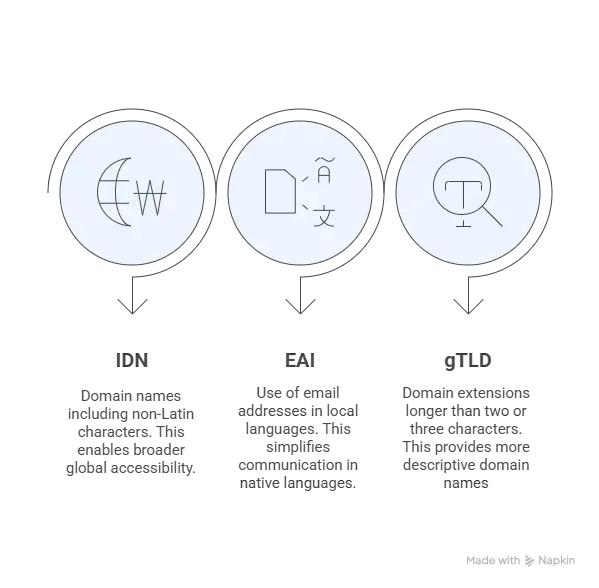
- Internationalized domain names (IDN): domain names that incorporate non-Latin characters, such as Arabic, Chinese, Cyrillic, or Devanagari.
- Email address internationalization (EAI): the ability to use email addresses in local scripts and languages, facilitating communication in native tongues.
- Long top-level domains (gTLDs): domain extensions longer than the traditional two or three characters, such as .photography or .technology.
The introduction of these elements has significantly diversified the digital landscape. However, many legacy systems still assume that domain names and email addresses are limited to ASCII characters and short TLDs, leading to compatibility issues and excluding non-Latin scripts from the digital ecosystem.
Benefits of universal acceptance for businesses
For globally oriented businesses, adopting universal acceptance is not optional, it is essential. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced user experience: Customers can interact with digital platforms in their native scripts, building trust and engagement.
- Market expansion: By supporting a wider range of languages and scripts, businesses can access previously untapped markets, driving growth and innovation.
- Legal compliance: In jurisdictions where digital inclusivity is mandatory, UA compliance is crucial for meeting regulatory requirements.
- Brand protection: UA-compatible infrastructure safeguards brand identity across diverse linguistic and cultural contexts.
Legal implications and considerations
From a legal perspective, universal acceptance has significant implications:
- Intellectual property rights: Protecting trademarks and domain names across multiple scripts requires a deep understanding of UA standards and their application.
- Contractual obligations: Agreements with clients, partners, and service providers may require UA compliance to ensure seamless digital interactions.
- Dispute Resolution: Legal disputes related to domain name registration in non-Latin scripts may require specialized knowledge of the principles of Universal Acceptance and their application.
These extrajudicial procedures (such as the UDRP, ADR, and Syreli procedures) require technical expertise to address issues related to Unicode characters and the compatibility of domain name management systems. A specialized approach is essential to effectively resolve these disputes.
Legal professionals must stay informed about developments in UA to provide accurate advice and effectively safeguard clients’ digital interests.
The role of ICANN and available resources
The Internet Corporation for assigned names and numbers (ICANN) leads global efforts to promote Universal Acceptance through several initiatives:
- Universal acceptance steering group (UASG): a community-driven initiative aimed at raising awareness and facilitating UA adoption.
- Universal acceptance training programs: ICANN offers resources and training to help organizations understand and implement UA principles effectively.
- UA readiness reports: annual assessments that provide a global overview of UA adoption and highlight areas for improvement.
Steps to achieve universal acceptance readiness
Organizations can take several measures to ensure compliance with Universal Acceptance:
- System evaluation: Review existing systems and applications for compatibility with IDN and EAI.
- Staff training: Equip technical teams with the knowledge and skills needed to implement UA standards.
- Internal policies: Develop internal policies to promote and enforce UA compliance.
- Stakeholder engagement: Collaborate with industry groups, legal advisors, and regulators to stay updated on UA developments and best practices.
Conclusion
Universal Acceptance is a key element in the evolution toward a truly inclusive and accessible Internet. For businesses and legal professionals, adopting Universal Acceptance standards is not merely a technical update but a strategic decision aligned with global digital trends and regulatory expectations. By embracing Universal Acceptance, organizations can improve user experience, expand their reach into new markets, and ensure legal compliance in an increasingly diverse digital landscape.
Dreyfus Law firm assists its clients in managing complex intellectual property cases, offering personalized advice and comprehensive operational support for the complete protection of intellectual property.
Dreyfus Law firm is partnered with a global network of lawyers specializing in intellectual property.
Nathalie Dreyfus with the assistance of the entire Dreyfus team.
FAQ
1. What is Universal Acceptance?
It is the recognition and support of all domain names and email addresses, regardless of script or length.
2. Why is it important for businesses?
It enables access to international markets and improves user experience.
3. Which types of domain names are concerned?
Internationalized Domain Names (IDNs) and long top-level domains (gTLDs).
4. Does Universal Acceptance have legal implications?
Yes, it affects trademark protection and contractual obligations related to domains and emails.
5. How can organizations prepare for Universal Acceptance?
By evaluating systems, training staff, and implementing internal policies aligned with UA standards.
6. What domain name disputes are related to Universal Acceptance?
They often involve cybersquatting, trademark infringement, or domain registrations in non-Latin scripts, requiring expertise in Universal Acceptance.