Sommaire
Introduction
With the rise of online shopping, not only are buying habits changing, but so are methods of fraud. Return fraud, which involves sending back a counterfeit item instead of an authentic product, is now one of the most serious types of fraud.
This mechanism introduces counterfeits directly into legal distribution channels and undermines the integrity of inventories. As a result, companies can no longer rely on simple visual checks: sustainable trademark protection requires enhanced traceability and authentication tools, in line with best practices recommended by French and European authorities.
How return fraud works?
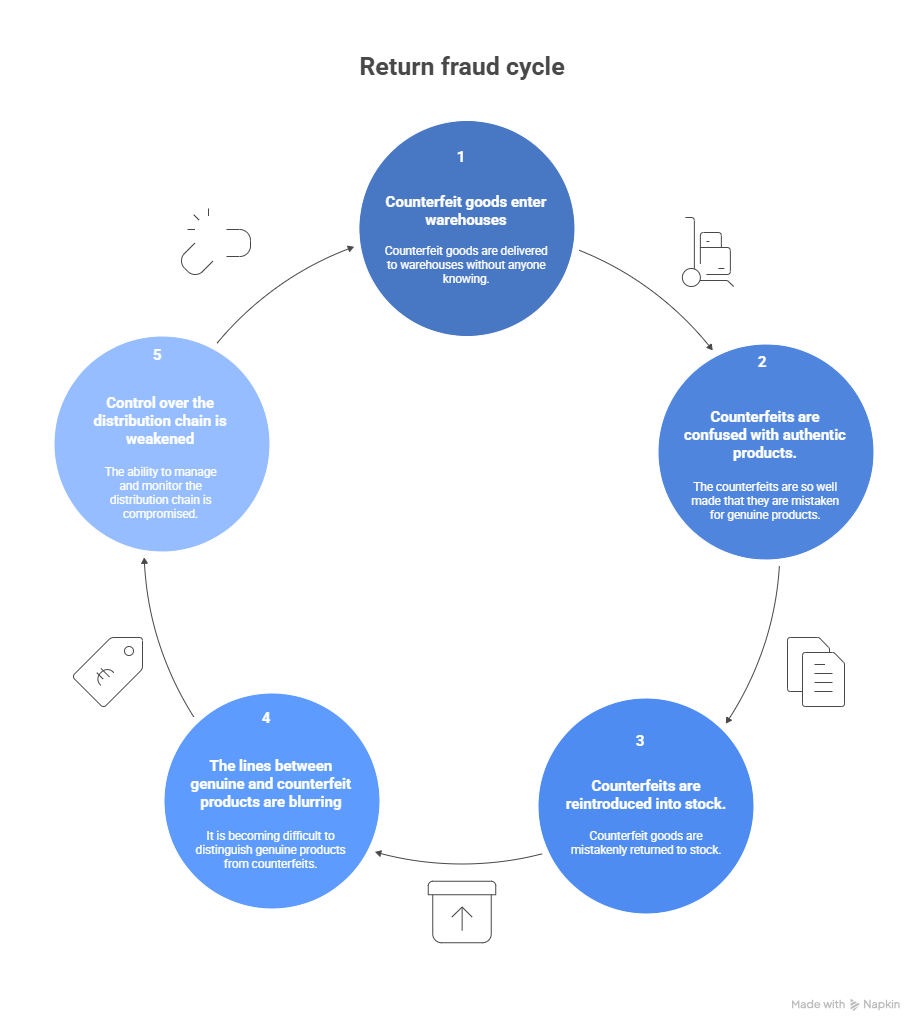
Return fraud is based on a simple but discreet strategy. The fraudster orders a genuine product, keeps the original, and returns a carefully reproduced imitation. This type of fraud thrives due to several factors:
- Very permissive return policies on e-commerce platforms,
- Increasing sophistication of counterfeits,
- Logistical pressure linked to large volumes,
- Lack of thorough checks upon receipt.
In warehouses, processing times are short and teams do not always have the expertise to identify high-quality fakes.
Why is return fraud rising in e-commerce?
Historically, counterfeit goods entered the market through parallel channels. Today, return fraud creates an internal entry point: counterfeit goods enter directly through the trademark‘s official channel. As a result:
- Warehouses receive counterfeits without their knowledge;
- Some counterfeits perfectly imitate the characteristics of the authentic product;
- Counterfeits may be mistakenly shipped to other consumers.
This confusion blurs the lines between authentic and counterfeit, complicating overall control of the supply chain.
Legal, financial, and reputational impacts
Return fraud has three major consequences:
- An immediate financial cost
The company loses the original item and is left with a counterfeit that cannot be sold. On a large scale, the losses add up.
- Significant reputational risk
If a counterfeit item is accidentally returned to a customer, trust is eroded, which can lead to complaints, doubts about quality, and damage to the company’s image.
- Significant legal consequences
The presence of counterfeits in the supply chain complicates infringement actions, as the break in traceability alters the evidence. This raises questions about civil liability, as well as the company’s ability to enforce its intellectual property rights.
Strengthening authentication and traceability
To limit this risk, companies must adopt enhanced technical mechanisms:
- Unique digital identifiers for each item,
- Discreet markings applied during manufacturing,
- Authentication technologies integrated into the product,
- Digital tracking of the item’s life cycle until its eventual return.
Internal procedures must allow for rapid and confidential verification of authenticity upon receipt.
A sustainable protection strategy
Return fraud evolves with online commerce practices. Companies must therefore secure the entire chain:
- Production,
- Transport,
- Distribution,
- Returns.
But the strategy must also be based on:
- Robust internal procedures,
- Regular updates to the legal framework,
- Ongoing training for teams,
- Constant risk analysis to anticipate new methods.
Conclusion
Return fraud is now a major challenge for businesses. It is essential to implement robust authentication systems and strengthen return controls. Companies that invest in these measures protect their reputation, the value of their assets, and public trust in the long term.
Dreyfus & Associés assists its clients in managing complex intellectual property cases, offering personalized advice and comprehensive operational support for the complete protection of intellectual property.
Nathalie Dreyfus with the support of the entire Dreyfus team
FAQ
1. What is return fraud?
The purchase of an authentic product followed by the return of a counterfeit or different product.
2. Why is this phenomenon rising?
Due to flexible return policies, the increasing quality of counterfeits, and the rise in return volumes.
3. What are the risks for businesses?
Risk of financial loss, damage to reputation, and legal difficulties related to the presence of counterfeits in the supply chain.
4. How can you protect yourself?
Through unique identifiers, authentication technologies, digital tracking, and strict internal procedures.
5. Is it possible to completely eliminate return fraud?
No, but consistent measures can greatly reduce the risk.